Mixed Convection equations
(Lagrée P.-Y.) à jour 06/04
LMM-Univ PARIS 6, B 162,
4 place Jussieu, 75252 PARIS
pyl@ccr.jussieu.fr
The thermal mixed convection boundary- layer flow over a flat horizontal
cooled plate is revisited. It is shown that this flow is very similar to
what happens in a free convection hypersonic boundary layer and that the
observed branching singular solutions may be reinterpreted in the framework
of ''triple deck''.
In fact this is very similar to what happens in an hydrolic jump (in water),
so this problem is a kind of hydrolic jump in thermal flow.
Two saillant structures emerge, one in double deck, if
the buoyancy is very small, and an other in single deck, if the buoyancy is
of order one: this is a reinterpretation of Steinrück results. A
numerical simulation of the unsteady boundary layer in the case of the
impulsively started and cooled plate is done, it leads to the separation of
the boundary layer as predicted by triple deck.
Incomming flow at temperature T0 and velocity U0
---> ---> --->
---> ---> --->
---> ---> ---> |
---> ---> --> |
---> --> -> | gravity
---> ====================================================== |
v
Flat Plate at Temperature Tw
There is a competition between the forced convection and
the buoyancy induced natural convection.
(Tw-T0) L Re-1/2
J is the Richardson Parameter: J = g a ---------------
U02
This parameter gauges the mixed convection effect.
If the temperature of the wall is lesser than the temperature of the flow,
a self induced separation appears.
The system to solve:
òu òv
-- + -- = 0
òx òy
òu òu òu òp ò2u
-- + u -- + v -- = - -- + ---
òt òx òy òx òy2
òp
0 = - -- + J T
òy
òT òT òT ò2T
-- + u -- + v -- = ---
òt òx òy òy2
u=v=0 T=1 on the wall
u=1 T=0 far over the plate.
òp/òx=0 at the output.
The final steady state depends of the size of the
computational domain. If it is enough large, a separated bulb may be created.
Preceding results stopped just before the point a zero skin friction.
Thanks to triple deck, it may be shown that this flow is not
"parabolic": there is up stream influence (like in hypersonic flows).
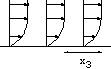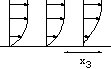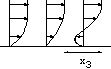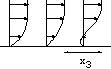
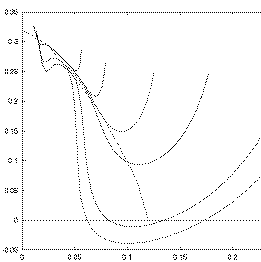 the reduced skin friction function of the domain size, results are
compared with the calculation of Wickern 1991 (compiled by Steinrück
and refered as ''marching''. The size of the domain is xout=5 10 20 50 and 125.
The boundary layer separation is obtained (separation buble).
the reduced skin friction function of the domain size, results are
compared with the calculation of Wickern 1991 (compiled by Steinrück
and refered as ''marching''. The size of the domain is xout=5 10 20 50 and 125.
The boundary layer separation is obtained (separation buble).
 the displacement thickness function of the domain size, from the
nose to x=15. (The size of the domain is xout=5 10 20 50 and
125).
The thermal hydrolic jump may be observed as the "jump" of the displacement thickness
where is the separation buble.
the displacement thickness function of the domain size, from the
nose to x=15. (The size of the domain is xout=5 10 20 50 and
125).
The thermal hydrolic jump may be observed as the "jump" of the displacement thickness
where is the separation buble.
Publications on this subject
P.-Y. Lagrée (2001):
''Removing the marching breakdown of the boundary layer equations for
mixed convection above a horizontal plate'',
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol 44, pp 3359-3372.
P.-Y. Lagrée (2001):
"Disparition de la singularité de convection
thermique mixte sur une plaque horizontale
refroidie.",
Cong. F. de Thermique, SFT 2001, Nantes.
le poster.
P.-Y. Lagrée (2000):
"Convection thermique mixte sur une plaque horizontale refroidie: disparition
de la singularité",
Journées de Metz, 04-05 mai 2000.
Earlier publications, the Triple Deck aspect
P.-Y. Lagrée (1994):
''Convection thermique mixte à faible nombre de Richardson dans
le cadre de la triple couche'',
C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris, t. 318, Série II, pp. 1167- 1173, 1994
P.-Y.
Lagrée (1994):
''Upstream influence in mixed convection at small Richardson Number
on triple, double and single deck scales'',
symp.: Asymptotic Modelling in Fluid Mechanics, Bois, Dériat,
Gatignol & Rigolot (Eds.), Lecture Notes in Physics, Springer, pp.
229-238.
Lagrée P.-Y (1994):
"Mixed convection at small Richardson number on triple deck scales",
Communication à "International Conference on Asymptotics in
Mechanics St Petersburg 14-17 August 94."
P.-Y. Lagrée (1994):
"Influence amont dans un écoulement de convection thermique
mixte à faible nombre de Richardson dans le cadre de la théorie
de la triple couche",
journée d'étude sur "les phénomènes chaotiques
et la transition en convection thermique" du 16 mars 1994 de la
Société Française des Thermiciens.
Publication on a linked subject: Mixed convection in Poiseuille flow
(Double Deck)
P.-Y. Lagrée (1999):
''Thermal mixed convection induced locally by a step in surface temperature
in a Poiseuille Flow in the framework of Triple Deck'',
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 42 pp. 2509-2524.